Company news
Exploring the Inner Workings Principle of a Dissolved Oxygen Sensor
Writer: admin Time:2024-05-14 15:28:49 Browse:1070℃
Dissolved oxygen (DO) refers to the amount of oxygen dissolved in water. The level of dissolved oxygen in water is a crucial indicator of water quality and a key factor in water purification.
The dissolved oxygen sensor in water can precisely measure the concentration of dissolved oxygen in a water sample and monitor real-time changes in the dissolved oxygen concentration within the water body. So, this water quality analysis instrument is widely used in aquaculture, wastewater treatment, environmental monitoring, etc.
Currently, methods for measuring dissolved oxygen include polarography, galvanic cell, and fluorescence methods.
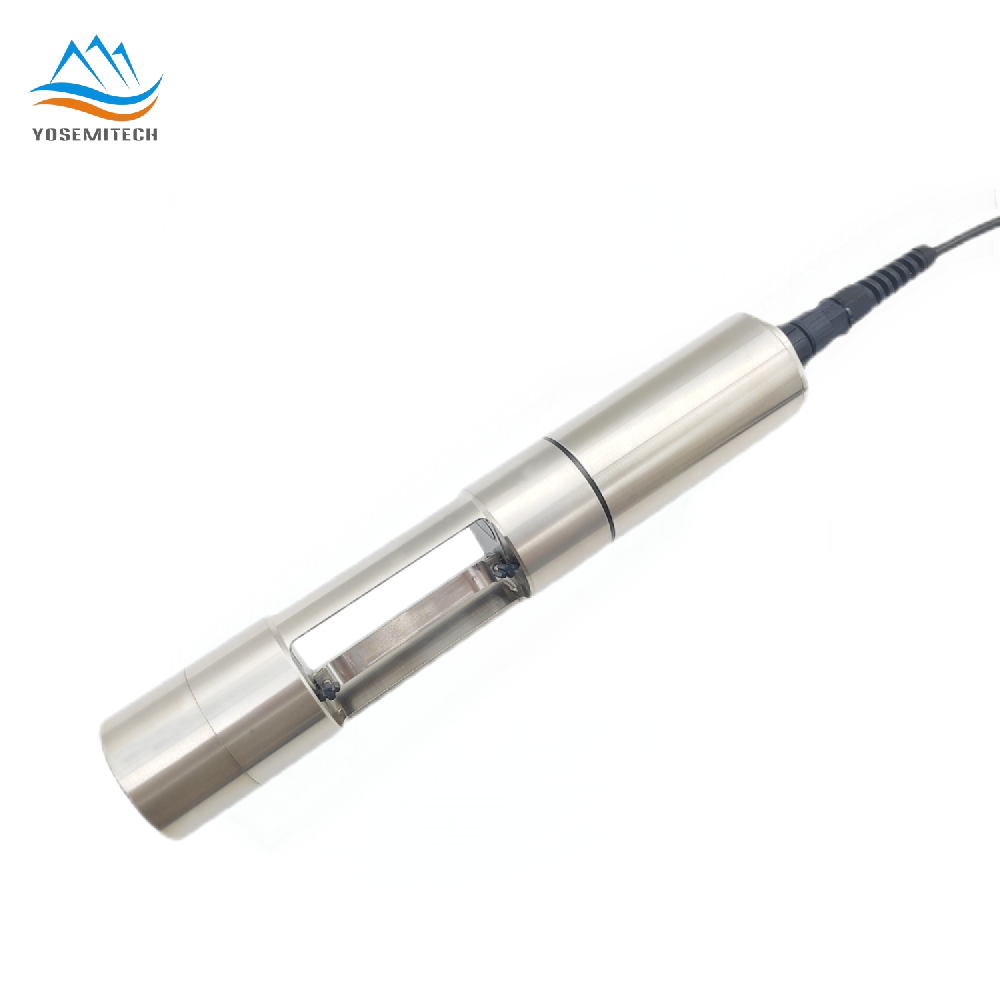
The polarographic sensor consists of a silver anode and a ring-shaped gold cathode at the bottom. A thin semipermeable membrane is spread over the sensor to isolate the electrode from the outside while allowing gas to enter. During operation, the bottom of the sensor is filled with an electrolyte containing a small amount of surfactant to improve the wetting effect. When a polarizing voltage is applied to the electrodes of a polarographic sensor, oxygen penetrates the membrane and reacts at the cathode, producing an electric current. The current flowing through the electrode is proportional to oxygen, and there is a linear relationship between current and oxygen concentration when the temperature remains constant.
When galvanic DO sensor is immersed in water sample, oxygen that diffuses across the oxygen-permeable membrane at a rate proportional to the pressure of oxygen in the water is reduced and consumed at the cathode. This reaction produces an electrical current that is directly related to the oxygen concentration. This current is carried by the ions in the electrolyte and runs from the cathode to the anode.
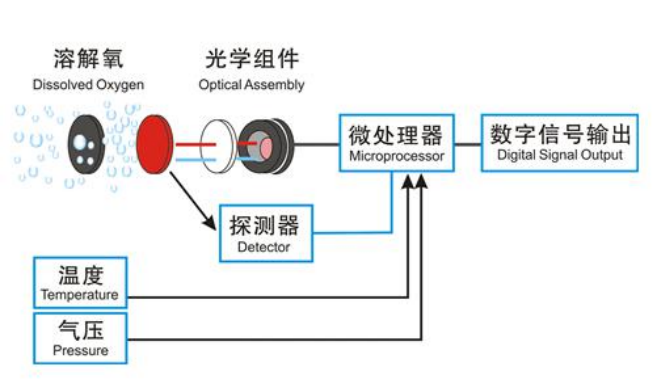
The fluorescence dissolved oxygen sensor is based on the quenching principle of active fluorescence by specific substances in physics. The blue light emitted from a light-emitting diode (LED) illuminates the fluorescent material on the inner surface of the fluorescent cap. The fluorescent material on the inner surface is excited and emits red light. The phase difference between the red light and the blue light is detected and compared with the internal calibration value. Compare to calculate the concentration of oxygen molecules, and automatically compensate the temperature and pressure to output the final value.
CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
Yosemitech Technologies Co., Ltd
 +86 19984844080
+86 19984844080
 sales@yosemitech.com
sales@yosemitech.com
 Bldg,25,CECEP Industrial Park, No. 18 Dongchang Rd. Suzhou Industrial Park, Jiangsu Province,China 215126, China
Bldg,25,CECEP Industrial Park, No. 18 Dongchang Rd. Suzhou Industrial Park, Jiangsu Province,China 215126, China







