FAQ
How Does Temperature Affect Dissolved Oxygen?
Writer: admin Time:2023-12-21 10:05:11 Browse:4713℃
What is Dissolved Oxygen (DO)?
Dissolved oxygen (DO) refers to oxygen content in water, which aquatic organisms rely on for survival. This free oxygen, not bonded to other elements, is crucial for the respiration of fish, invertebrates, and microorganisms living in water.
Why is Dissolved Oxygen So Important?
Aquatic Respiration: Just as land animals need oxygen in the air to breathe, aquatic organisms extract this dissolved oxygen from the water. Low levels can lead to stress or even fatalities in these organisms.
Ecosystem Indicator: The level of dissolved oxygen is a vital parameter of water quality. High DO levels generally signify healthy water bodies, while low levels can indicate pollution, excessive organic decay, or eutrophication.
Wastewater and Drinking Water: In industries like wastewater treatment and drinking water purification, monitoring dissolved oxygen helps ensure that treatment processes are effective and that the water meets safety standards.
Sources of Dissolved Oxygen
They are two main sources of dissolved oxygen in water: Atmospheric Diffusion and Photosynthesis by Aquatic Plants.
Atmospheric Diffusion
The air surrounding us is composed of about 21% oxygen, which gradually seeps into the water through a process called diffusion. This happens when oxygen molecules move from the air into the water, balancing the concentration on both sides.
Natural Aeration: This occurs through wind action, which helps mix the air and water, enhancing oxygen diffusion.
Human-Induced Aeration: Practices such as using waterwheels, pumps, and dams can also increase the amount of oxygen that penetrates the water.
Photosynthesis by Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants, including phytoplankton and algae, play a pivotal role in oxygenating water. Through photosynthesis, these plants convert sunlight into energy, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. This oxygen dissolves directly into the water, adding to its overall oxygen content.
However, this dissolved oxygen doesn't stay indefinitely. It's consumed through processes like:
Chemical Oxidation: Interactions involving dissolved substances in the water.
Respiration: Conducted by fish and other aquatic organisms.
Decomposition: Breakdown of organic materials, which uses up oxygen.
Factors affecting dissolved oxygen (DO) in water
The amount of dissolved oxygen in water is related to both the partial pressure of oxygen in the air and the temperature of the water.
① Barometric pressure. The relationship between dissolved oxygen and barometric pressure is directly proportional. So how do you go about determining barometric pressure? Do you read the weather forecast every day? Of course not, it is not that troublesome to judge the barometric pressure. The simplest way is when we feel very boring weather, that is, low air pressure, the pond is easy to lack of oxygen, we should pay attention to the oxygen, open the aerator.
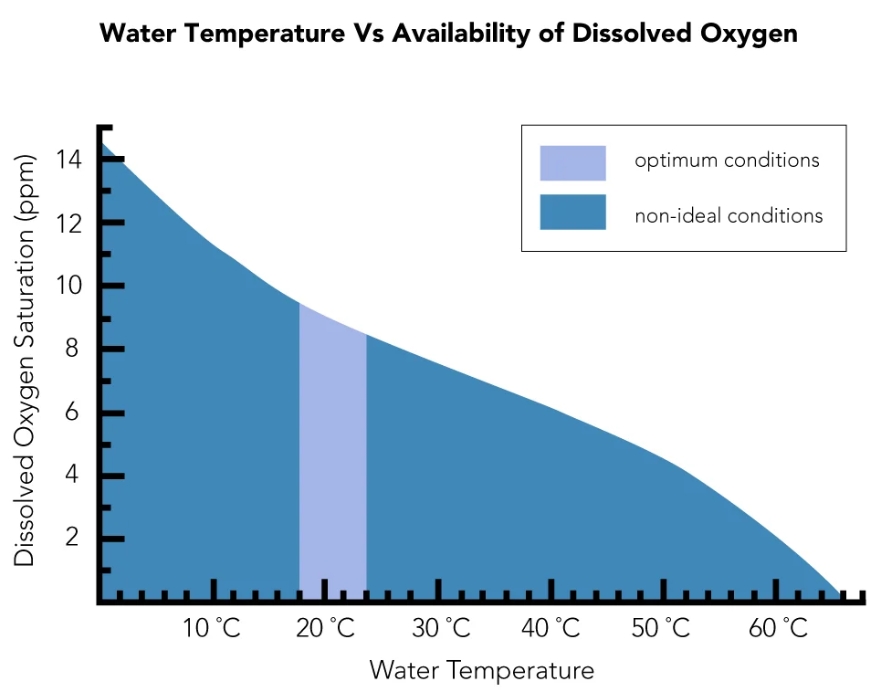
② Temperature and salinity. Dissolved oxygen is inversely proportional to these two factors, the lower the water temperature, the higher the content of dissolved oxygen in the water. The higher the salinity, the lower the content of dissolved oxygen in the water. Freshwater generally has higher dissolved oxygen than seawater.
③ Sunlight. The level of dissolved oxygen is directly proportional to the intensity of sunlight (within a certain intensity range), mainly because the stronger the sunlight, the more oxygen produced by photosynthesis.
④ Breeding density. Dissolved oxygen is inversely proportional to culture density. If the breeding density of a pond is too high, the more serious the oxygen depletion is, the less dissolved oxygen will be in the pond relatively speaking.
⑤ Transparency. Dissolved oxygen is inversely proportional to transparency (within a relative range).
⑥ Substrate (organic matter). Dissolved oxygen is inversely proportional to organic matter. If there is too much organic matter in the pond, the more severe the oxygen depletion. The lower the relative DO content.
How Does Temperature Affect Dissolved Oxygen?
Saturated dissolved oxygen concentration in water and its corresponding temperature | |||||
temperature | DO(ppm or mg/L) | temperature | DO(ppm or mg/L) | ||
℉ | ℃ | ℉ | ℃ | ||
32 | 0 | 14.6 | 74 | 23.3 | 8.5 |
34 | 1.1 | 14.1 | 76 | 24.4 | 8.3 |
36 | 2.2 | 13.7 | 78 | 25.6 | 8.2 |
38 | 3.3 | 13.3 | 80 | 26.7 | 8.0 |
40 | 4.4 | 12.9 | 82 | 27.8 | 7.8 |
42 | 5.6 | 12.2 | 84 | 28.9 | 7.7 |
44 | 6.7 | 11.9 | 86 | 30 | 7.5 |
46 | 7.8 | 11.6 | 88 | 31.1 | 7.4 |
48 | 8.9 | 11.3 | 90 | 32.2 | 7.3 |
50 | 10 | 11.0 | 92 | 33.3 | 7.1 |
52 | 11.1 | 10.7 | 94 | 34.4 | 7.0 |
54 | 12.2 | 10.4 | 96 | 35.6 | 6.9 |
56 | 13.3 | 10.2 | 98 | 36.7 | 6.8 |
58 | 14.4 | 9.9 | 100 | 37.8 | 6.6 |
60 | 15.6 | 9.7 | 102 | 38.9 | 6.5 |
62 | 16.7 | 9.5 | 104 | 40 | 6.4 |
64 | 17.8 | 9.3 | 106 | 41.1 | 6.3 |
66 | 18.9 | 9.1 | 108 | 42.2 | 6.2 |
68 | 20 | 8.9 | 110 | 43.3 | 6.1 |
70 | 21.1 | 8.7 | 112 | 44.4 | 6.0 |
72 | 22.2 | 114 | 45.6 | 5.9 | |
Dissolved oxygen in water at standard atmospheric pressure as a function of temperature and salinity (dissolved oxygen mg/L) | |||||||||
Temp (℃) | Salinity | ||||||||
0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | |
20 | 9.1 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 7.2 |
22 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.2 | 8 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.9 |
24 | 8.4 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.9 | 6.7 |
26 | 8.1 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.4 |
28 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 6.2 |
30 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6 |
32 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.8 | 6.7 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 6.1 | 6 | 5.8 |
34 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 6.3 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 5.8 | 5.6 |
36 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 5.4 |
38 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 5.5 | 5.4 | 5.2 |
40 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 5.9 | 5.8 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5 |
How Do Increased Water Temperatures Affect Aquatic Ecosystems?
Rising water temperatures have a profound impact on aquatic ecosystems, influencing everything from oxygen levels to nutrient availability.
Reduction in Dissolved Oxygen
As water heats up, both gas and water molecules gain energy. This energetic shift disrupts molecular interactions, allowing oxygen to escape into the atmosphere. Furthermore, warmer water inherently holds less dissolved oxygen (DO). This scenario not only heightens water pollution but also stresses aquatic habitats, putting organisms at risk.
Effect on Aquatic Life
When DO levels plummet to critical levels (below 3 mg/L), the water becomes hypoxic—a state detrimental to most aquatic life. In such conditions, mobile organisms might relocate to oxygen-rich areas, but those in confined environments like aquariums and ponds are left with no escape. These organisms, including fish, often face fatal outcomes.
Nutrient Solubility and Algal Blooms
Elevated temperatures also impact the solubility of essential nutrients. This can lead to an imbalance, causing nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen to be released from sediment. These fluctuations might shift the water's pH and prompt excessive algal blooms, which worsen the situation by depleting further oxygen, perpetuating a cycle of decline.
Impact on Fish Populations
The life cycle of fish is particularly sensitive to changes in water temperature and DO levels. Lower oxygen levels hinder the development of fish embryos, leading to reduced egg hatching rates and impaired larval development. Over time, these factors can severely diminish fish populations, with widespread implications for aquatic food chains and fisheries.
In summary, the ripple effects of increased water temperatures severely compromise aquatic ecosystems, affecting both biological and chemical processes critical to maintaining healthy water environments.
Impact of Low Dissolved Oxygen Levels on Water Treatment Systems
Low dissolved oxygen (DO) levels can significantly disrupt the efficiency of both wastewater and drinking water treatment systems.
Wastewater Treatment
Microbial Imbalance: In wastewater systems, maintaining a balanced ecosystem is crucial. Low DO levels, particularly those below 1 mg/L, can trigger the overgrowth of filamentous bacteria. This imbalance suffocates beneficial aerobic and nitrifying microbes essential for breaking down waste, leading to operational challenges and potentially degraded water quality.
Impact on Water Settling: While filamentous bacteria thrive, other required microbial processes falter, causing poor settling of sludge. This can result in cloudy effluent and increased handling costs.
Drinking Water Treatment
Dissolution of Minerals: When oxygen levels drop in drinking water systems, minerals can dissolve more readily into the water supply. This can lead to undesirable changes in water quality, such as taste alterations and possible health concerns from contaminants.
Corrosion and Infrastructure Concerns: Although higher DO levels might improve taste, there’s a risk of increased pipe corrosion as oxygen promotes rust formation. Therefore, it becomes critical to balance DO levels to avoid costly infrastructure damages, while still providing safe, high-quality drinking water.
Balancing the right DO levels is crucial in both systems, ensuring effective treatment processes and maintaining water quality without incurring additional costs.
How to Measure Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen in Water?
To Measure Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
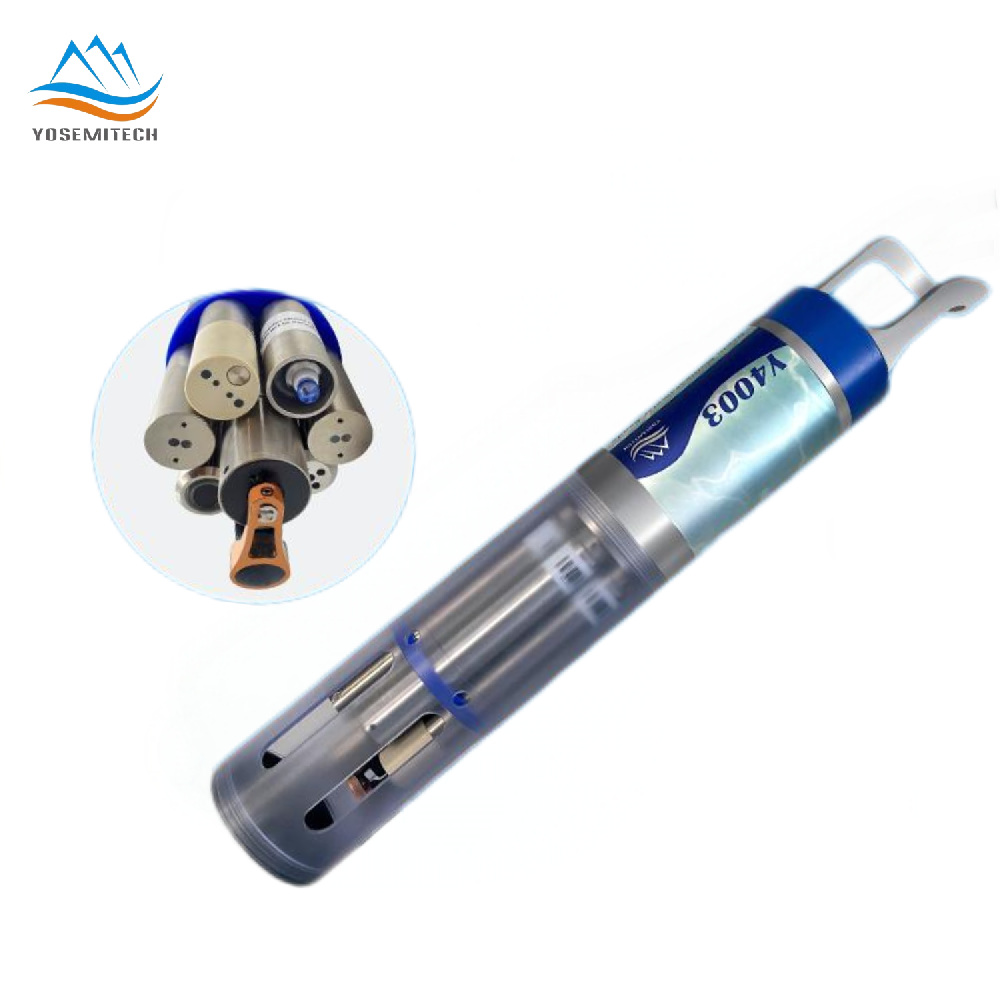
Usually, we use optical dissolved oxygen probes to detect the dissolved oxygen content in water. Yosemitech Optical Do Sensors use high-efficiency fluorescent membranes, don't consume oxygen, no flow limit. Built-in temperature sensors, automatic temperature compensation. It has excellent accuracy and stability.

https://e.yosemitech.com/DO/Y504-A.html
To Measure Temperature
Temperature sensors are recommended to accurately measure temperature levels in the water. Temperature probes work by providing readings via electrical signals.
CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
Yosemitech Technologies Co., Ltd
 +86 19984844080
+86 19984844080
 sales@yosemitech.com
sales@yosemitech.com
 Bldg,25,CECEP Industrial Park, No. 18 Dongchang Rd. Suzhou Industrial Park, Jiangsu Province,China 215126, China
Bldg,25,CECEP Industrial Park, No. 18 Dongchang Rd. Suzhou Industrial Park, Jiangsu Province,China 215126, China







